| USP No | Functional group | USP Description | YMC Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| L01 | C18 | Octadecyl silane <ODS or C18> chemically bonded to porous silica or ceramic particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Triart C18 |
| L03 | SIL | Porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | |
| L07 | C8 | Octyl silane <C8> chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Triart C8 |
| L08 | NH2 | An essentially monomolecular layer of aminopropylsilane <NH2> chemically bonded to totally porous silica gel support – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Pack NH2 |
| L10 | CN | Nitrile groups <CN> chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Pack CN |
| L11 | Ph | Phenyl groups chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Triart Phenyl |
| L13 | C1 | Trimethylsilane <C1> chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Pack TMS |
| L20 | Diol | Dihydroxypropane groups chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Triart Diol-HILIC |
| L24 | Polyvinyl alcohol | Polyvinyl alcohol chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 5 µm in diameter | YMC-Pack PVA-Sil |
| L26 | C4 | Butyl silane <C4> chemically bonded to porous silica particles – 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Triart Bio C4 |
| L27 | SIL | Porous silica particles – 30 to 50 µm in diameter | YMC-Pack SIL-HG |
| L33 | Diol | Packing having the capacity to separate dextrans by molecular size over a range of 4,000 to 500,000 Da. It is spherical, silica-based, and processed to provide pH stability | YMC-Pack Diol (SEC) |
| L40 | Cellulose derivatives |
Cellulose tris-3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate coated porous silica particles, 3 to 20 µm in diameter | CHIRAL ART Cellulose-C |
| L43 | PFP | Pentafluorophenyl groups chemically bonded to silica particles by a propyl spacer, 1.5 to 10 µm in diameter | YMC-Triart PFP |
| L51 | Amylose derivatives |
Amylose tris-3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate-coated, porous, spherical, silica particles, 3 to 20 µm in diameter | CHIRAL ART Amylose-C |
| L59 | Diol | Packing for the size exclusion separations of proteins (separation by molecular weight) over the range of 5 to 7000 kDa. It is spherical (1.5 to 10 µm), silica or hybrid packing with a hydrophilic coating | YMC-SEC-MAB |
| L62 | C30 | C30 silane bonded phase on a fully porous spherical silica, 3 to 15 µm in diameter | YMC Carotenoid |
| L99 | Amylose derivatives |
Amylose tris-(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate), immobilized on porous, spherical, silica particles, 3 to 5 µm in diameter | CHIRAL ART Amylose-SA |
| L111 | Polyamine | Polyamine chemically bonded to porous spherical silica particles, 5 µm in diameter | YMC-Pack Polyamine II |
| L119 | Cellulose derivatives |
Cellulose tris-(3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate), immobilized on porous, spherical, silica particles, 3 to 5 µm in diameter. | CHIRAL ART Cellulose-SC |






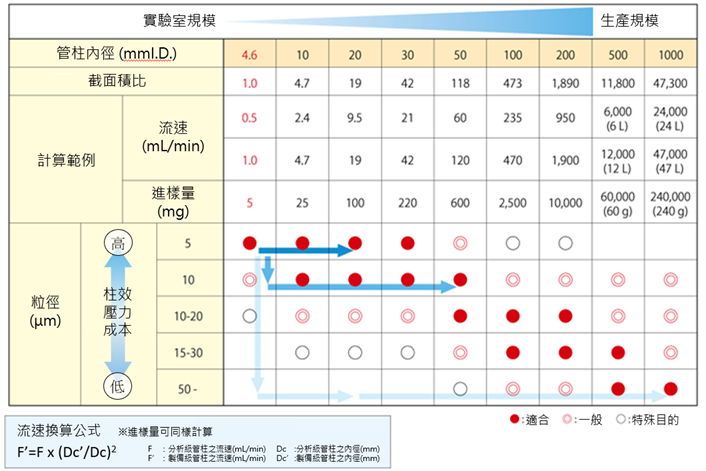
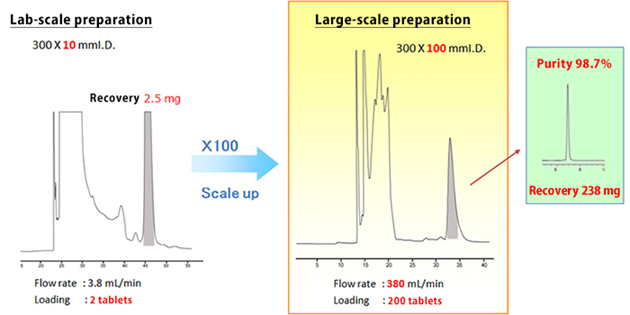


近期留言